United Kingdom (1)
Title of the survey
Short-Term (Monthly and Quarterly) Employment Statistics
Organization responsible
Employment Department, Statistical Services Division, Branch D2.
Periodicity of the survey
Monthly for production industries, and quarterly for agriculture,
construction and service industries.
Objectives of the survey
To provide monthly and quarterly information on employment levels
according to industrial activity and location of individual workplaces,
at national and regional levels. This information is used by government
ministries, Prime Minister, policy branches, statistical branches,
Treasury, academics and others, for monitoring employment trends.
Main labour topics covered by the survey
Employment and hours of work.
Reference period
For employment, a specific day each month or quarter.
For hours of work, a specific week each month or quarter.
Coverage of the survey
Geographical
The monthly survey of production industries covers Great Britain only.
The quarterly surveys cover the whole of the United Kingdom and provide
separate data for the whole country, Great Britain and standard regions.
Industrial
All divisions of economic activity, except the armed forces. However,
some divisions are not covered by employer-based surveys, but data for
them come from administrative centralized returns provided by
government departments (e.g. construction is covered by the Department
of Environment survey) and other large organizations (e.g. Post Office,
the London and Scottish Clearing Banks Association).
Establishments
All types and sizes of establishments or data units.
Persons
Monthly estimates cover production workers (manual workers, operatives)
in manufacturing.
Quarterly estimates cover employees in employment.
Excluded are working proprietors and working directors, unpaid family
workers and young workers below the age of 16.
Occupations
All occupations are covered but none are separately identified. The
only occupational groups that are separately identified are
operatives and administrative, technical and clerical
staff in manufacturing.
Concepts and definitions
Employment
The data refer to employees in employment. This is a count
of civilian jobs of employees paid by employers who run a
"Pay-As-You-Earn" (PAYE) income tax scheme. Employees include wage
earners and salaried employees; permanent, temporary and casual
employees; apprentices, trainees and workers on probation; persons
temporarily absent from work because of paid or unpaid vacation,
sickness or accident, temporary or indefinite lay off, industrial
dispute, or any other reasons, whether authorized or not; and employees
who work away from the workplace such as sales representatives and lorry
drivers. Participants in Government employment and training schemes are
included if they have an employment contract. As the estimates of
employees in employment are derived from employers' reports of the
number of people they employ, individuals holding two jobs with
different employers will be counted twice.
Excluded from employees in employment are private domestic servants,
piece workers, home workers and commission agents; persons temporarily
present on payroll during notice period preceding retirement,
resignation or dismissal; former employees still on the payroll as
pensioners; persons on temporary military service; those employed by
outside contractors or agencies, and employees who normally work at
another establishment such as temporary transfers and secondments.
The following categories of workers are identified separately:
- manual workers (operatives), who are production workers,
maintenance, warehouse and transport workers and foremen (except works
and other higher level foremen);
- administrative, technical and clerical staff, who include managers,
administrative, professional, scientific, technical, clerical and sales
employees;
- part-time operatives, who are persons normally working for not more
than 30 hours a week except where otherwise stated;
- operatives on lay off during the reference
week;
- operatives on short-time;
- operatives working overtime.
Earnings
Not relevant.
Wage/salary rates
Not relevant.
Hours of work
Data are collected on hours lost on short-time and
on overtime hours
worked by operatives in manufacturing and in Great Britain only.
Hours lost on short-time refer to those arrangements made
by an employer for working less than regular hours (i.e. less than
the normal weekly hours specified in national collective agreements
or statutory wages orders for manual workers). Short-time working
excludes time lost through sickness, holidays, absenteeism and the
direct effect of industrial disputes.
Overtime hours refer to hours outside normal hours, for
which a premium rate is paid.
Data on hours lost on short-time working and on overtime hours are
collected separately for full-time and part-time operatives.
Data are not collected on normal hours of work.
Classifications
Industrial
Employees are allocated to the activity code of the establishment or
data unit in which employed, and classified according to the
Standard Industrial Classification (SIC), 1980. This classification is
not linked to the International Standard Industrial Classification of
all economic activities (ISIC), Revision 2, 1968. However, the recent
revision (SIC-1992) is convertible to ISIC, Revision 3, 1990.
Occupational
Not relevant.
Others
The survey data are also classified according to:
- standard region (Borough of Greater London, county in England
and Wales, administrative region in Scotland);
- sex (only employment data);
- full-time and part-time workers.
Sample size and design
Statistical unit
The sampling and reporting unit is the data unit, i.e. a
specific PAYE paypoint at a single site which belongs to a single
industry. So a company with a corporate headquarters and four branch
offices is regarded as five separate sampling units, each of which could
be chosen independently for inclusion in the panel survey. If one of
the branch offices has two paypoints (one for salaried staff and one
for weekly paid staff) there would be six units and again each
unit would have an independent chance of selection.
Survey universe / sample frame
The sampling frame consists of the Pay-As-You-Earn (PAYE) income
tax records of employers, maintained by the Inland Revenue.
Income tax records are updated constantly, but with a certain time-lag,
when the tax authorities are notified by employers.
Sample design
The sample is designed around a core, called the main panel,
augmented with a quarterly top-up of newly created business
units, after recording units which have closed.
The main panel is designed as a sub-set of all companies which responded
to the last Census of Employment (the present main panel is based on the
1991 census), stratified by region, industry and number of employees.
Each panel member is then approached for up-to-date information on the
number of employees. A random sample of data units is drawn within each
stratum.
In order to take account of the creation of new companies, the main
panel is supplemented by quarterly Inland Revenue information on the
quarterly registration of PAYE schemes by employers. This information
identifies new PAYE paypoints which are examined and sometimes
approached to see if they fall within the boundary of the new units.
Those which do are sampled to provide a suitable top-up of new
units to add to the main panel. The sampling method is similar to that
used to identify the original main panel, i.e. a stratified sample by
region, industry and size.
Each quarter, approximately 30,000 units are in the sample (i.e. about
three per cent of all units and 33 per cent of employment), with a
monthly sub-sample of 6,000 units in the manufacturing and production
industries.
The sample consists of over 6,000 strata and the sampling fraction
varies with each stratum. Large companies and organizations
(generally those with 1,000 or more employees, sometimes those with 250
or more employees) are included with certainty.
The sample drawn from businesses accounts for about two thirds of all
employees. The remainder are covered by a separate system of
centralized returns whereby complete details on employment in certain
industries are collated each quarter and sent in by one central point
within the industry.
The sample is updated every quarter, using the information provided
by the Inland Revenue tax records.
Sample rotation is not used.
Field work
Data collection
This takes place each month or quarter. Questionnaires
are mailed to the sample units up to two weeks prior to the reference
date. Reminder forms are issued for non-responding units and phone
contacts are made for queries.
Survey questionnaire
This incorporates the statutory notice under the Statistics
of Trade Act, 1947, and instructions on definitions, inclusions and
exclusions with regard to each question. Different questionnaires are
used for different industries; in general, they include questions
on:
- number of employees, by sex, full-time and part-time, and reasons
for important changes in numbers since last return;
- number of operatives, hours lost on short-time working and number
of overtime hours (only in manufacturing);
- number of administrative, technical or clerical staff, by sex;
- reason(s) why the business has stopped;
- contact name for further queries.
Substitution of sampling units
There is no substitution of sampling units in the case of total
non-response.
Data processing and editing
Data are processed by computer, and the forms are entered by batch onto
the data base. Data checking and editing involves computer-generated
queries with respect to credibility or comparison with
data for the previous month or quarter.
Part-time workers are counted as a separate category contributing
to the total in the same way as full-time workers. No allowance is
made for differing amounts of hours worked. Missing data are dealt
with by imputation or allowed for in the grossing-up procedure.
Types of estimates
- total of employees, for the month or quarter;
- total of operatives (in manufacturing);
- totals and averages of overtime hours and hours lost by short-time
work.
Construction of indices
Overtime, short-time and employment data are combined with data on
normal hours of work derived from the New Earnings Survey, to produce an
index of average and total hours worked by operatives in manufacturing.
Weighting of sample results
The employment estimates are weighted on the basis of the latest
Census of Employment, according to the following formula:
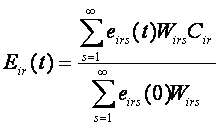
where,
- Eir(t)=
- employment estimate for industry i, region r, at time t,
- Cir(t)=
- Census estimate,
- s=
- size range,
- W=
- weight,
- eirs(t)=
- sample employment at time t,
- eirs(0)=
- sample employment at Census time.
Adjustments
Non-response
There is no adjustment for non-responses. Employers are required
by law (under the 1947 Statistics of Trade Act) to furnish replies
to the questionnaires.
Other bias
No adjustments are made for any other bias.
Use of benchmark data
The estimation formula (see above) includes benchmark information
on the basis of the latest Census of Employment.
Seasonal variations
Data are seasonally adjusted, using the X-11 programme. Additive
factors are produced for employment, and multiplicative factors are
produced for hours. Forward factors are used for one quarter, then the
programme is re-run and the previous quarter is revised. There is also
an annual review of seasonal factors to produce consistent series.
Indicators of reliability of the estimates
Coverage of the sampling frame
Coverage is virtually complete. PAYE income tax records are updated
constantly, but with a certain time-lag, when the tax authorities are
notified by employers.
Sampling error / sampling variance
Not available.
Non-response rate
In manufacturing, the monthly non-response rate averages 13 per cent
and the quarterly non-response rate is approximately 15 per cent.
In the services, it is around 13 per cent.
Non-sampling errors
The main known sources of bias relate to possible duplications or
omissions from the benchmark (Census of Employment), incorrect data
received from employers, errors in keying the data or in clearing the
queries.
Conformity with other sources
In the past (up to 1991), the survey results were compared with the
results of the annual Labour Force survey and adjustments were made to
the survey results to bring the annual rates of change in line with the
LFS. This practice has been discontinued and the new panel of employers
designed in 1992 is expected to track the real economy accurately and
provide estimates that are both timely and reliable. The series of
employees in employment are then revised retroactively on the basis of
the next Census of Employment (as this was the case in 1993, on the
basis of the results of the 1991 census).
Available series
Published tables include estimates of employees in employment
- by industry, sex and full- or part-time;
- by industry and region;
- by industry, sector and full- or part-time (seasonally adjusted and
non-adjusted);
and estimates of overtime and short-time operatives and hours in
manufacturing, including monthly indices.
History of the survey
The Short-Term Statistics of Employees in employment started in
1971.
Various changes were made to the layout of the questionnaires at various
times, but the same information has been collected.
Periodically, estimates of employees in employment are revised on the
basis of the latest Census of Employment. The 1991 census introduced a
change in the collection of data for employees working for local
authorities, which had implications on the estimates for industrial
series.
In March 1992 a new panel of employers was selected. At the
same time, estimation techniques and allowance for non-response were
also modified.
Changes planned for the next few years include:
- improvements to the Register of Employers and adoption of a business
register (EDBR) common to all Employment Department employment surveys;
- change in industrial classification in 1995;
- faster processing of survey documents by optical character
recognition technology;
- new short-term estimates rebased on the 1993 Census of Employment;
- earlier close-down of short-term surveys.
Documentation
Employment Department: Employment Gazette (monthly, London).
Monthly employment and hours data in manufacturing are published some
eight to ten weeks after the survey reference period. Quarterly data in
services and data for the whole economy, including that part of the
workforce in employment not covered by the surveys, 14 to 16 weeks after
the reference period.
Additional data which do not appear in publications can be made
available upon request, in the form of ASCII files,
LOTUS-123 or SUPERCALC spreadsheets, CSV, etc., on diskette.
Confidentiality / Reliability criteria
The Statistics of Trade Act, 1947, under which the survey is conducted,
prohibits the publication of information about indentifiable individuals
or units. The information supplied by employers is never disclosed
to any unauthorised person without their consent.
Other information
Data supplied to the ILO for publication
Estimates of employees in employment form part of the employment
estimates published in Tables 3A to 5B of the Yearbook of Labour
Statistics.
Quarterly employment series are published in Tables 1 to 3 of the
Bulletin of Labour Statistics.
Statistics.