Hong Kong, China (2)
Title of the survey
Survey of Wages, Salaries and Employee Benefits
Organization responsible
Census and Statistics Department
Periodicity of the survey
Half-yearly, in March and September.
Objectives of the survey
- To compile nominal wage indices for individual industries analysed
by broad occupational group as well as for all the industries covered as
a whole, in order to measure the changes in wage rate in money terms;
- To derive real wage indices by deflating the nominal wage indices by
the Consumer Price Index, for measuring the changes in purchasing power
of wages; and
- As a by-product, to compile statistics on the absolute level of
prevailing wage rates and normal hours of work of principal occupations
in the major industries, for reference in career counselling and salary
determination.
Main labour topics covered by the survey
- number of employees
- wage rates
- normal hours of work per day
- standard working days per month
for each selected occupation in each industry.
In addition, about once every two years, information is collected on
establishment pay practices in terms of employee entitlements to various
types of benefits other than wage rates.
Reference period
Employment: the last working day of the reference month.
Wage rates and hours of work: the whole month of March and September
for salaried employees; a fixed day for wage earners, (i.e. the last
normal working day of the month).
Coverage of the survey
Geographical
The whole territory.
Industrial
Since the March 1993 survey, 46 selected industries are included,
covering: manufacturing, electricity and gas, wholesale, retail and
import-export trades, restaurants and hotels, transport and
communication services, business services and personal services.
Establishments
Medium and large establishments above a pre-set size of employment which
is determined separately for each industry. In general, establishments
with less than 10 persons employed are excluded.
Persons
Employees up to the supervisory level, aged 15 years and over.
Proprietors, family workers and out-workers who work in their own
premises are excluded.
Occupations
In each selected industry, a number of occupations which have clearly
understood and definable duties are surveyed if they are either
numerically important or identified as being of special interest.
Individual occupations are those classified under the following two
occupational groups:
- Supervisory, technical, clerical and miscellaneous non-production
workers, and
- Craftsmen and operatives.
Managerial and professional level occupations are excluded from the
scope of the survey.
Concepts and definitions
Employment
Data refer to full-time employees directly paid by the
establishment, whose duties and tasks correspond to the selected
occupations. The main categories of employees covered in the survey are
time-rated and piece-rated workers. Within these categories, workers of
both sexes are included. Time-rated employees cover all employees paid
on a time basis, whether this be hourly, daily, weekly, fortnightly or
monthly.
For monthly-rated employees, only those receiving a full month's salary
in the reference month are included. For daily-rated and piece-rated
employees, only those working on the reference date are included.
Employees who are paid less than the established wage rates, such as
handicapped workers whose wage rates are reduced because of their
handicap, part-time workers, apprentices, learners, trainees and workers
on probation are not covered.
Data are also collected on the total number of persons
engaged by the establishment on the last working day of the
reference month. This includes working proprietors and business
partners, and all full-time employees, both permanent and temporary, who
are either at work or temporarily absent from work on the reference
date, because of sick leave, maternity leave, annual vacation or casual
leave, and on strike. Part-time employees and unpaid family workers who
work more than three hours on the reference date are also included.
Excluded from persons engaged are persons on indefinite leave and on
pension, and outworkers who work in their own premises on materials
supplied by the establishment.
Earnings
Not relevant.
Wage/salary rates
They comprise the following elements:
- basic wages and salaries, including paid holidays and leave
- commission and tips (excluding tips received directly from
customers)
- shift allowance
- cost-of-living allowance
- meal allowance and meal benefits
- good attendance bonus
- guaranteed year-end bonus, and
- other regular and guaranteed bonuses and allowances
About once every two years, information is collected on establishment
pay practices in terms of employees' entitlements to various types of
benefits other than wage rates. These include:
- paid holidays per annum
- housing benefits
- provident fund
- pension scheme
- medical benefits
- profit-sharing bonuses
- rates of overtime premium, and
- other benefits
Hours of work
Data are collected on normal hours of work per day.
They refer to the hours of work, excluding meal breaks and rest
time, stipulated by the establishment for each occupation, and beyond
which any time worked is remunerated at overtime rate or forms an
exception to the rules and customs of the establishment.
Data on wage rates and normal hours of work cover the same categories of
employees as employment data and are collected separately by sex and
mode of payment for each selected occupation in each industry.
Data are also collected on the number of standard working
days per month, by sex and mode of payment, for each selected
occupation in each industry.
If there is no rest days granted at all in a month, the number of
standard working days is 30. Where rest days are granted on a monthly
basis, the number of standard working days is the difference
between 30 and the number of rest days granted in a month. If rest days
are granted on a weekly basis, the assumption of four weeks in a month
is made.
The standard working days per week are calculated as follows:
- 26 working days per month correspond to 6 days a week,
- 24 working days per month correspond to 5 1/2 days a week,
- 23 working days per month correspond to working half days on
alternate Saturdays,
- 22 working days per month correspond to five days a week.
International recommendations
The components of wage and salary rates mentioned above conform to the
international recommendations on wage rates. They refer to the rates
actually paid by the establishment for the specified occupations during
the reference period, and comprise basic wage rates as well as
guaranteed and regularly paid allowances.
The concept of normal hours of work used in this survey conforms to the
international guidelines.
Classifications
Industrial
Data on wage and salary rates and normal hours of work are classified
according to the Hong Kong Standard Industrial Classification (HSIC) and
selected industries are coded mainly at the four-digit level of this
classification. The HSIC can be linked to the International Standard
Industrial Classification of all economic activities (ISIC), Rev. 2,
1968 at the four-digit level, with some slight modifications.
Occupational
Data on wage and salary rates and normal hours of work are classified
according to the International Standard Classification of
Occupations (ISCO-68). Individual occupations are selected from
major groups 3, 4, 5, 7, 8 and 9 and classified according to the
following occupational groups and subgroups:
- Supervisory, technical, clerical and miscellaneous non-production
workers:
- supervisory and technical workers
- clerical and secretarial workers
- service workers, and
- miscellaneous non-production workers
- Craftsmen and operatives:
Occupational classifications and job specifications are defined in
advance of the survey. The job specifications may differ significantly
from those in use in individual establishments. In order to improve the
inter-establishment comparability of occupational content, the primary
objective of the job specifications is to identify the essential
elements of skill, difficulty and responsibility that establish the
basic concept of the job.
Others
Data on wage and salary rates and hours of work are also classified by
sex and mode of payment.
Sample size and design
Statistical unit
The sampling and reporting unit is the establishment, defined
as an economic unit which engages, under a single ownership or control,
in one, or predominantly one kind of economic activity at a single
physical location.
The unit of inquiry is an occupation in an establishment
(and not the individual worker).
Survey universe / sample frame
This consists of the Central Register of Establishments
kept by the Census and Statistics Department. It covers all
non-agricultural establishments engaged in economic activities
classified under HSIC major divisions one to nine.
The Register is updated on a continuous basis to
take account of birth and death
cases, on the basis of data from the Business Registration Office,
administrative records and results from various economic surveys
of the Census and Statistics Department. For records which are new to
the Register, establishment particulars are collected by postal, then
field enumeration method. New insertions and amendments are updated
on a quarterly basis.
Sample design
The survey is based on a rotational stratified random sampling method.
A main sample is drawn from the frame once every two years.
It is stratified by industry and employment size and divided
into eight replicates. Four replicates are selected for each round of
the survey; each round, one replicate is replaced in order to spread
the burden of selected establishments, so that 75 per cent form an
overlapping sample for two consecutive rounds. A sample unit is thus
surveyed a maximum of four times and the whole sample is completely
renewed after two years.
Each round, the sample consists of some 2,000 establishments, with an
average of 50 establishments per industry, out of a total of some 7,000
establishments falling within the scope of the survey. This represents
an employment size of approximately 270,000 persons, out of some 680,000
employees.
The sampling fraction and sample size in terms of number of
establishments varies with each stratum. The sampling fraction ranges
between 7.55 and 50 per cent, and public utility companies
(i.e. electricity and gas and transport services such as motor buses,
tramways and ferries) are included with certainty.
Each round of the survey,
supplementary samples are chosen and incorporated into the main sample
in order to take account of death
cases (i.e. closed-down establishments, establishments that have fallen
below the minimum size limit and those that have changed the nature of
their business) and to incorporate birth cases (i.e. newly opened
establishments that fall within the scope of the survey and
establishments not previously within the scope of the survey that have
shifted in during the course of the survey).
Field work
Data collection
This takes place during the periods 1 April - 20 May (for the March
round) and 1 October-20 November (for the September round). At the
start of the survey round, notification letters are first sent out to
the sampled establishments. Field officers, who are members of a
permanent survey organization, then visit the respondents and assist
them in job matching and filling in the questionnaire.
Survey questionnaire
This consists of two parts and is complemented by explanatory notes
corresponding to most questions in the questionnaire.
Part A provides general establishment information such as name, main
product or activity, total number of persons engaged, total number of
employees covered in Part B, and particulars of the establishment
covered in the questionnaire (name, address, business registration
number, etc.).
Part B is designed to provide occupational data on wages and salaries.
Respondents are required to fill in one form per occupation. For each
occupation, detailed information is required on the number of employees
covered, by sex and mode of payment, and for each sub-category, on the
following items: number of normal working hours per day; number of
standard working days per month; minimum and maximum basic wages and
salaries actually paid to employees and weighted average basic
wages/salaries; amount of each benefit listed under "Wage/salary
rates"; and item of work and normal output per day for piece-rated
employees.
Substitution of sampling units
There is no substitution of sampling units in case of total
non-response (due to refusal, establishments which have closed
down or moved with an unknown address, etc.).
Data processing and editing
Data are processed both manually and by computer. Coding of occupation
is done manually; coded data are transcribed onto data preparation
forms according to coding instructions. Data are checked first
manually, then through computer programmes. Three types of checks are
made: (i) level checks for overlapping replicates, to check whether the
change in wage rate is acceptable, (ii) range check for all replicates,
to check whether wage rates are within an acceptable range, and
(iii) logical check on individual data items for internal
consistency.
Individual occupations with missing fields are discarded.
Starting from the March 1993 survey round, data from a certain
proportion of establishments are input directly into laptop computers
during field enumeration and validated on the spot. For the other
establishments, data are collected using the conventional pen and paper
method and input into the computer (with on-line validation) by indoor
staff. The input data are then further checked by computer programmes
to detect outliers.
Types of estimates
The survey is designed to estimate both the changes in and the levels of
wage rates. Three types of estimates are derived from the survey:
- average daily wage rates and monthly salary rates,
- nominal and real wage indices, and
- median, and lower and upper quartiles of wage/salary rates.
Estimates are also made of mean normal hours of work per day and mean
number of standard working days per month.
Median and quartiles: since wage rates of individual workers are not
available through this survey, the computation of median and quartile
wages is based on the assumption that the average wage rate for a
particular occupation in a particular establishment is representative of
the wage rates of all workers in that occupation in that establishment.
Establishment pay practices: statistics on various benefits other than
wage rates are expressed in terms of the percentage of workers included
in the survey and entitled to the benefits.
Construction of indices
The Nominal Wage Index is calculated using a Laspeyres base-weighted
formula, so that occupational and industrial structure is held constant.
Starting from the March 1993 survey round, the base period is September
1992 and the weights were determined in the September 1992 survey
(previously, March 1982).
To compare wage
indices of the old series (March 1982=100) and those of the new series
(September 1992=100), a splicing method is used, whereby (i) a
conversion factor is derived from the indices for the overlapping period
of September 1992 in both index series, and (ii) the index for a
particular month with the old base period is converted to the new base
period by multiplying the index by the conversion factor.
The Real Wage Index is obtained by deflating the Nominal Wage Index by
the Consumer Price Index (A). Although the same deflator is used for
each industry to derive the real wage index from its nominal
counterpart, the difference between the movements of the nominal wage
index and the real wage index between any two time periods may vary
slightly from industry to industry, due to rounding.
Weighting of sample results
Average daily wage rate or monthly salary rate of a particular
occupation in a particular industry is given by the ratio of the
estimated total wage bill for that
category of workers to the estimated total number of workers in that
category, according to the following simplified formula:
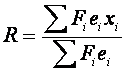
where,
- R=
- average wage rate for employees of a certain sex and mode of payment of a particular occupation in a particular industry;
- Fi=
- grossing-up factor for the ith establishment;
- ei=
- reported number of employees in that category in the ith establishment;
- xi=
- reported average wage rate of employees in that category in the ith establishment.
For calculating average wage rates for higher levels of aggregation
(e.g. an occupation, an occupational group, a particular industry and
all industries combined), the same method is used, extending the
summation sign in both the numerator and the denominator to cover all
workers in the required level of aggregation.
Adjustments
Non-response
Since the March 1993 survey, non-response is taken into account by
adjusting the sampling fractions so that in effect, the values of
stratum averages are imputed for the non-response cases.
Other bias
Changes in industrial classification are accounted for by adjusting the
sampling fraction.
Use of benchmark data
Not relevant.
Seasonal variations
Not relevant.
Indicators of reliability of the estimates
Coverage of the sampling frame
Total coverage of all non-agricultural establishments engaged in
economic activities is aimed at. The Central Register of Establishments
covered some 480,000 establishments as at December 1990.
Sampling error / sampling variance
The coefficient of variation of daily and monthly
wage/salary rates
at broad occupational group level mostly ranges between five
and ten per cent.
The sampling variance is computed as follows:
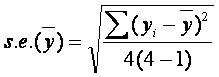
where, for four independent replicates,
- yi=
- estimate for the ith replicate,
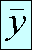 =
=
- overal estimate =
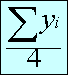 .
.
Non-response rate
It averages 9 per cent, in terms of refusals, closed-down establishments
or establishments which moved to an unknown address, etc.
Non-sampling errors
The following remarks should be taken into account when
interpreting the estimates:
- Sample size: a sample of 2000 establishments cannot bear detailed
analysis. The detailed breakdowns of wage rates for individual
occupations are therefore given for rough guidance only.
- Changes in wage rates: as a result of changes in sample composition
and staff movement, the movement of the absolute level of wage rates may
differ slightly from the movement of the wage indices. Where this
happens, the wage indices should be used as indicator of changes;
- Wage indices: the wage indices are designed to measure the "pure"
changes in wage rates by holding constant the structure of the labour
force with respect to industry, occupation, sex and mode of payment
between two successive rounds of the survey. However, it is not
possible to standardize the experience and quality of workers within the
basic unit which is defined by an occupation, sex and mode of payment.
Hence, changes in composition of workers in terms of experience and
quality within a basic unit may still distort, though not significantly
so at the higher levels of aggregation, the movements of the wage
indices;
- Wage rates of piece-rated workers: a time basis is used to measure
piece-rated wages. When asking for piece-rated wages, the normal output
of an average worker within a certain time period is obtained together
with the rates per unit of output. An assumption is made that there is
sufficient work for the worker to work unceasingly within the time
period. In view of this, the wage rate of piece-rated workers should
not be used to calculate actual earnings.
- Linking wage index series of different base periods: the method
used to compare wage indices of old and new series should be applied
with particular care in comparisons at the economic sector level and the
"all industries" level, in view of the fact that the coverage of some
industries may be different for the two index series, and the industry
coverage of each economic sector has been revised in 1992.
Conformity with other sources
A reconciliation of the survey results is made with the findings of
the Index of Payroll Per Person Engaged by industry group, obtained
from the Survey of Employment, Vacancies and Payroll (SEVP).
Available series
Two sets of data are tabulated:
- summary statistics in the form of short-term economic indicators,
relating to nominal and real wage indices analysed by industry and broad
occupational group, and by economic sector and occupational group, and
medians and quartiles of daily wages and monthly salaries analysed by
economic sector and broad occupational group;
- detailed results on average daily wages and average monthly
salaries, normal hours of work and standard working days, separately for
craftsmen and operatives, and for supervisory, technical, clerical
and other non-production workers, analysed by industry, occupation and
sex; as well as percentage of each category of workers entitled to
various benefits other than wage rates, analysed by industry.
History of the survey
The Survey of Wages, Salaries and Employee Benefits was introduced in
March 1982 on a quarterly basis to replace the old Wage Survey which
had been conducted since 1964 at half-yearly intervals. At that time, a
number of improvements were made, which included:
- the use of a larger sample (from 350 to some 2,000 establishments)
to achieve a higher degree of precision in the estimates,
- an extension in coverage to include the non-manufacturing sectors (a
total of 41 industries were covered, representing most economic sectors)
and non-manual workers (i.e. supervisory, technical, clerical and
miscellaneous non-production workers),
- adoption of the rotational sampling method, in order to reduce the
burden on respondents, and
- collection of more detailed information.
After the September 1989 survey round, the frequency of the
survey was changed to half-yearly.
In 1992, a review of the survey was undertaken with a view to improving
the survey design. As a result, the industrial coverage has been
updated, mainly by dropping some declining manufacturing industries and
adding industries in the services sector which have grown in importance.
The occupational coverage has also been updated. Moreover, improvements
to the sample design, estimation methods and questionnaire design have
been introduced. A parallel run of the new and old survey design
was conducted in September 1992. Starting from the March 1993 round,
wage statistics are published based on the new survey design and the
base period of the wage indices changed from March 1982 to September
1992.
Since March 1994, the collection of payroll statistics has been
transferred from the Survey of Employment, Vacancies and Payroll to the
Survey of Wages, Salaries and Employee Benefits. The latter is
subsequently renamed Labour Earnings Survey.
Documentation
Census and Statistics Department: Report on Half-yearly Survey of
Wages, Salaries and Employee Benefits, volumes I and II
(half-yearly, Hong Kong). The first volume includes summary statistics
in the nature of short-term economic indicators and the second volume
contains detailed occupational wage data. They are published some 3.5
months after the survey reference period. Both volumes contain
methodological information on the survey. Starting from the March 1993
survey round, the content of the report and the table layouts have been
slightly modified.
idem: Hong Kong Monthly Digest of Statistics (monthly. ibid.);
the survey results appear in this publication some 5.5 months after the
survey reference period.
idem: Hong Kong Annual Digest of Statistics (annual, ibid.);
published some 14 months after the survey reference period.
Ad hoc requests for data which do not appear in national publications
are handled on a case-by-case basis by the Census and Statistics
Department.
Confidentiality / Reliability criteria
Statistics compiled from data collected from less than ten
establishments are suppressed from publication because either (a) data
are insufficient to provide meaningful statistical results, or (b) there
is a possibility of disclosure of individual establishment data.
Other information
Data supplied to the ILO for publication
Statistics of average daily wage rates in non-agricultural activities,
manufacturing, construction and transport, storage and communication
are provided each year for publication in
the Yearbook of Labour Statistics.
Statistics of average monthly wage rates in trades, restaurants and
hotels, financing, insurance, real estate and business services, as well
as personal services, are contained in the ILO data base and available
upon request.
Half-yearly series of average daily wage rates (wage earners) and
monthly wage rates (salaried employees) in non-agricultural activities
and manufacturing are published in Tables 7 and 8 of the Bulletin of
Labour Statistics.
Statistics of average basic daily wage rates,
average basic monthly salary rates and normal hours of work, as well as
average wage and salary rates including fringe benefits, by occupation
and industry, are published in
Statistics on occupational wages and hours of work and on food
prices - October Inquiry results, a special supplement to the
Bulletin of Labour Statistics.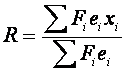
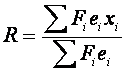
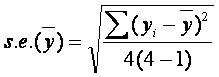
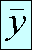 =
=
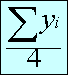 .
.