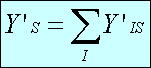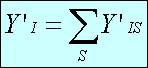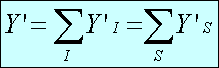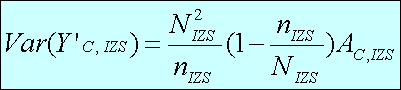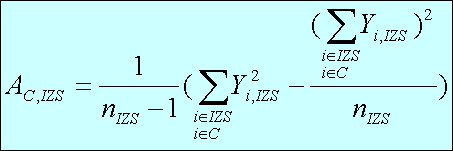Malaysia (1)
Title of the survey
Annual survey of manufacturing industries
Organization responsible
Department of Statistics
Periodicity of the survey
Annual
Objectives of the survey
The survey results are used mainly to determine the growth, composition
and distribution of manufacturing at the five-digit level of industry,
and to measure the various costs, inputs and outputs for manufacturing.
They are also used for economic projections and for compiling national
accounts.
Main labour topics covered by the survey
Employment, earnings and compensation of employees.
Reference period
Employment: as at 31 December or the last pay period of the reference
year.
Earnings and compensation of employees: the calendar year, or the
accounting year if this is different from the calendar year.
Coverage of the survey
Geographical
The whole country.
Industrial
Manufacturing: the mechanical or chemical transformation of inorganic
or inorganic substances into new products, whether the work is performed
by power driven machines or by hand, whether it is done in the factory
or in workers' homes, and whether the products are sold at wholesale or
retail. The assembly of the component parts of manufactured products is
considered as manufacturing except in cases where the activities are
appropriately classified under Construction. Establishments primarily
engaged in repair work are included and classified according to the type
of product repaired.
Establishments
All establishments registered under the Industrial Co-ordination Act
(ICA) 1975, and all operating manufacturing establishments with
certain specified volume of employment, which varies according to
region and industry group.
All manufacturing establishments with a paid-up capital of 2.5 million
rupees or more and with 75 or more full-time employees are required to
register under the ICA. They are all covered in the survey regardless
of the lower limit on the volume of employment specified for each
industry group.
Persons
All persons engaged by the establishments covered.
Occupations
Not relevant.
Concepts and definitions
Employment
The data on employment are collected with respect to all
persons engaged, including working proprietors and active
business partners; unpaid family workers; and full-time and part-time
employees.
Working proprietors and active business partners: individual
proprietors and partners, part-time or full-time, who are actively
engaged in the work of the establishments. The following are excluded:
silent and inactive partners and members of the proprietors' family,
unless they participate in the control and management of the business.
Unpaid family workers: all persons of the household of any
of the owners of the establishment who perform a specified job
full-time or part-time, and who work for a minimum of one third of the
normal working time of the establishment, but do not received payment
either in cash or in kind for his or her work. Such workers generally
receive food, shelter and other support as part of the household of an
owner, but these provisions would continue whether they worked in the
establishment or not.
Paid employees: all persons who worked during the year in the
establishment and received pay, including persons working away from
establishment when paid by and under the control of the establishment
(e.g. travelling engineering representatives, travelling maintenance
and repair personnel), salaried managers and directors of incorporated
enterprises except when paid solely for their attendance at Board of
Directors' meetings.
Full-time employees: all workers who work for at least six
hours a day, and for at least 20 days a month.
Part-time employees: all workers who normally work for less
than six hours a day or less than 20 days a month.
Data are collected separately by sex and for working proprietors and
active business partners, unpaid family workers, part-time employees and
the following categories of full-time employees:
- managerial and professional: managers are those who decide or
participate in formulating the policy of the organization and plan,
organize and direct the interpretation and execution of policies; their
work involves the responsibility for their organization as a whole or
for more than one department of an organization; professionals are those
who conduct research and apply in a professional capacity scientific
knowledge and methods to a variety of technological, economic, social,
industrial and government problems; the term applies generally to
persons required to hold professional qualifications to practise (e.g.
lawyers, accountants, doctors, chemists and engineers); classified as:
- professionals, including managers who are professional by virtue of
their qualifications; and
- non-professionals: managers who do not hold any professional
qualifications;
- technical and supervisory workers: technical workers are those
engaged in technical research and quality control work among other
activities; they usually work under the direction and supervision of
professionally qualified personnel (e.g. laboratory technicians,
quality control technicians, nurses and draughtsmen); supervisory
workers
are those who supervise various activities or a particular kind of
activity (e.g. production activity within an establishment); they
control
and coordinate the activities of the workers under their charge;
- teachers: professionals and non-professionals who teach in
schools, colleges and institutions;
- clerical and related workers: those who compile and maintain
records of financial transactions and other business activities
including material and production planning, handle cash on behalf of the
organization and its customers, record oral or written matter by
shorthand writing, typing and other means, e.g. clerks, typists,
stenographers, personal secretaries, bookkeepers and storekeepers.
- general workers: those who perform general and miscellaneous
functions, of whom:
- ushers and ticket sellers;
- drivers, conductors and lorry attendants;
- others (e.g. telephone operators, office attendants, security
guards, gardeners, etc.);
- other directly employed workers: the balance of the full-time paid
employees employed directly by the establishment and not included
elsewhere, e.g. factory, construction, mine and stevedoring workers,
classified as skilled, semi-skilled or unskilled;
- workers employed through labour contractors; classified as skilled,
semi-skilled or unskilled.
Earnings
Data are collected on wages and salaries, relating to
the value of money payments, including bonuses, cash allowances, etc.
made to all paid workers during the calendar year, whether or not all
workers were still on the payroll at the end of that year.
Amounts are recorded gross, before deductions for employees'
contributions to the Employees' Provident Fund (EPF).
Allowances to working proprietors, working partners and unpaid family
workers are not included.
Data are collected separately by sex for the same categories of worker
as the employment data.
Compensation of employees
In addition to earnings, data are also collected on payments in
kind paid to employees, the value of free wearing apparel
provided and employers' contributions.
Payments in kind cover the cost of goods and services
furnished to employees free of charge, or at markedly reduced cost,
which are primarily of benefit to the employees as consumers. Outlays
by employers which are of benefit to them as well as their employees,
e.g. expenditure by employers on amenities provided at the place of
work, sports and other recreational facilities and reimbursements by
employers of the expenses of travel, entertainment and work clothing,
tools and equipment which are incurred by their employees are excluded.
Data are collected separately on the following items, for all employees
together:
- free medical attention;
- free food;
- free accommodation;
- other payments in kind.
The value of free wearing apparel covers items such as
uniforms, overalls and work clothes; data are collected for all
employees together.
Employers' contributions relate to the following schemes, for
which data are collected separately, for all employees:
- Government provident funds: provident funds that are organized
and managed by the Government;
- other provident funds;
- Government social security schemes: social security schemes run by
the Government;
- private social security schemes.
Wage/salary rates
Not relevant.
Hours of work
Not relevant.
International recommendations
The definitions of earnings and compensation of employees conform to
those contained in the international recommendations.
Classifications
Components of labour cost / compensation of employees
Does not apply.
Industrial
The data are classified according to the Malaysia Industrial
Classification 1972 (updated 1979) at the five-digit level. If an
establishment is involved in a number of activities, of which there is
only one significant activity, the other activities are subsumed under
this activity and the establishment is classified in the industry of the
significant activity. If several significant activities are carried
out, the establishment is requested to submit separate returns for each
activity, and the data are classified accordingly.
The Malaysia Industrial Classification 1972 (updated 1979) can be
linked to the International Standard Industrial Classification of All
Economic Activities (ISIC), Revision 2, 1968 and Revision 3, 1990.
Occupational
Not relevant.
Others
The data are also classified according to:
- type of ownership (held by Malaysian residents: privately owned,
Government owned; held by non-Malaysian residents);
- employment size;
- size of fixed assets;
- volume of output;
- region.
Sample size and design
Statistical unit
The sampling and reporting unit is the establishment,
defined ideally as an economic unit which engages
under a single ownership or control in one or predominantly one kind of
industrial activity at a single location. If an establishment is
involved in more than one significant activity, in terms of value, it
is requested to submit separate returns for each activity. If an
establishment is involved in several activities, but only one of these
is significant in terms of value, the rest of the activities are
subsumed under this one activity.
Survey universe / sample frame
The survey frame is obtained from the Registrar of Companies (ROC) and
the Registrar of Businesses. It includes the list of establishments
registered under the Industrial Coordination Act (ICA) 1975, lists of
companies approved by the Malaysian Industrial Development Authority
(MIDA), the list of mills licensed by the Lembaga Padi dan Beras Negara
(LPN), etc.
The lists are updated each year to take into account new establishments,
those that have closed down and changes in correspondence addresses and
in the activities of the establishments. The updating process includes
sending screening questionnaires to the establishments and checking the
various administrative sources.
In 1992, the survey frame comprised 8,161 establishments.
Sample design
The survey is conducted as a census every five years, and on a sample
basis in the intercensal years. All establishments above the
specified cut-off based on the volume of employment are included. The
lower limit varies according to industry and region.
Field work
Data collection
Normally questionnaires are mailed out at the end of the February
following the reference year, and establishments are required to reply
within one month. If respondents fail to reply, a reminder is sent. If
that fails, field staff are sent out. In order to carry out the field
work effectively, the state branches of the Department of Statistics
have the responsibility of obtaining all replies from respondents.
In the case of non-response, information from the previous year is
usually used.
Survey questionnaire
This contains explanations of all items, and is
accompanied by detailed instructions for its completion. Information
is collected on the following:
- characteristics of the establishment (name, location, legal status,
type of ownership, reporting period and days worked by the
establishment, total overtime hours worked and wages paid for overtime,
principal activity and other activities);
- employment and payroll: total number of workers by citizenship and
ethnic group, and gross salary and wage payments, by category of worker
and sex;
- capital expenditure and value of fixed assets;
- value of production;
- income from property;
- expenditure (including the value of payments in kind and employers'
contributions) and consumption.
Substitution of sampling units
None.
Data processing and editing
After the questionnaires are returned to the respective state branches,
they are edited and coded manually. If no further query is necessary,
they are forwarded to the Headquarters, where they are checked and the
data entered on the computer and validated. The computer checks are
very comprehensive, and include range checks and consistency checks.
In the case of inconsistent data, queries are addressed to the
establishment.
There is no adjustment of data affected by abnormal circumstances, such
as strike, fire, flood, etc.
Types of estimates
Totals.
When the response rate reaches about 95 per cent in terms of the
number of units and about 99 per cent in terms of the estimated
output, the output of the smaller non-responding establishments
is estimated on the basis of averages calculated for respondents.
Simple unbiased estimation is used to calculate the desired
parameters and the variances.
Totals are calculated as follows:
State by industry:

State:
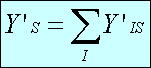
Industry:
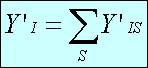
National:
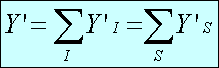
where:
- i
- establishment
- I
- industry
- Z
- size stratum
- S
- state
- NIZS
- population size of stratum Z of industry I in state S
- nIZS
- sample size
- wi,IZS=NIZS/nIZS
- survey weight for unit i in cell IZS.
Construction of indices
None.
Weighting of sample results
Not relevant.
Adjustments
Non-response
The results are not adjusted for non-response.
Other bias
The results are not adjusted for any other bias.
Use of benchmark data
Not relevant.
Seasonal variations
Not relevant.
Indicators of reliability of the estimates
Coverage of the sampling frame
About 21 per cent of the target population is covered by the survey
frame, in terms of the number of establishments, and about 72 per cent
in terms of employment.
Sampling error / sampling variance
The typical standard error is between 0.6 and 4.5 at the one-digit
level of industry.
Stratum level variances are calculated as:
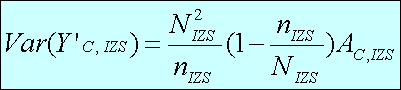
where:
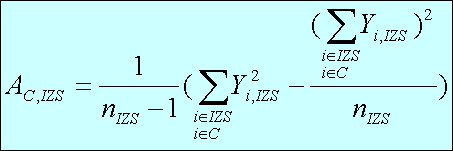
Non-response rate
The typical rate of non-response is about 5 per cent in terms of
establishments and about 1 per cent in terms of employment.
Non-sampling errors
Not relevant.
Conformity with other sources
The results are compared with data from the Monthly Manufacturing
Surveys.
Available series
The following tables are published regularly:
- principal statistics, by industry, state, legal
status, ownership, employment size group, output size group, fixed
assets size group
- employment payroll, by category of worker
- composition of output, by major industrial group
- composition of input, by major industrial group
History of the survey
The first survey, which was conducted on a census basis, took place
with reference to 1959. Subsequent censuses were carried out with
reference to 1963, 1968, 1973 and 1981.
In intercensal years, the
survey has taken place each year except 1980. It covers all large
establishments above a certain size (based on employment) and all those
registered under the ICA, except in 1988, when sampling was used.
The sampling design used was as follows:
All establishments registered under the ICA and all those above a
specified size, by industry, were included in the sample. Among
establishments below the specified lower limit for employment size,
(a) those in Sabah and Sarawak were all included, and (b) a sample
was selected for Peninsular Malaysia, except that industries with a
small number of establishments (less than 30) were all included.
Documentation
The results have been published in the following:
Department of Statistics: Survey of manufacturing industries
(annual; Kuala Lumpur) - prior to 1975 and from 1992 to present.
idem: Industrial surveys (annual; ibid.), 1975 to 1991.
Confidentiality / Reliability criteria
The statistics are subject to the Statistics Act 1965 (Revised 1989).
Other information
Data supplied to the ILO for publication
Data on paid employment in manufacturing are published in Tables 5A and
5B of the Yearbook of Labour Statistics.